ABP Framework-EventBus源码解析
https://abp.io/docs/6.0/Event-Bus
Version
6.0.3
Package
Volo.Abp.EventBus.Abstractions
Volo.Abp.EventBus //依赖Volo.Abp.EventBus.Abstractions
Volo.Abp.EventBus.Azure //依赖Volo.Abp.EventBus
Volo.Abp.EventBus.Kafka //依赖Volo.Abp.EventBus
Volo.Abp.EventBus.RabbitMQ //依赖Volo.Abp.EventBus
Volo.Abp.EventBus.Rebus //依赖Volo.Abp.EventBus
EventHandler
当某个事件发生,如果想要订阅事件,则是定义一个Handler来处理,ABP中经常使用的模式简要如下,以本地事件为例:
public class MyHandler : ILocalEventHandler<StockCountChangedEvent>, ITransientDependency
{
public async Task HandleEventAsync(StockCountChangedEvent eventData)
{
//TODO: your code that does something on the event
}
}
EventHandler从源头上便区分为LocalHandler和DistributedHandler以应付不同的使用场景。
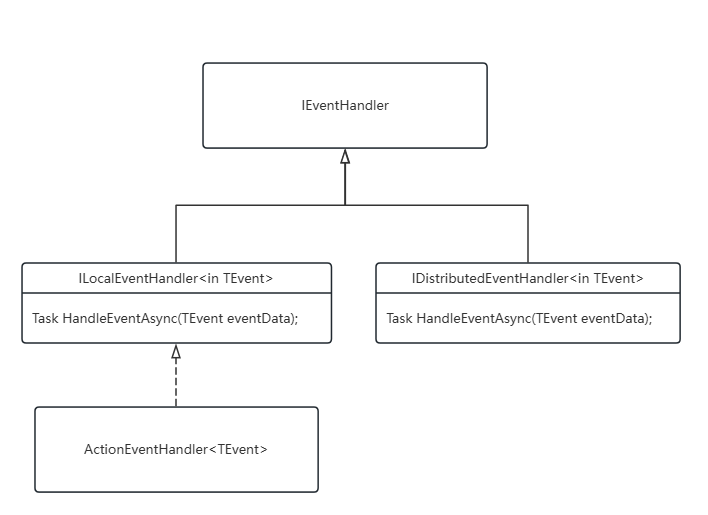 在项目启动阶段,在AbpEventBusModule中,会扫描所有LocalEventHandler和DistributedEventHandler分别注册到AbpLocalEventBusOptionsh和AbpDistributedEventBusOptions。
在项目启动阶段,在AbpEventBusModule中,会扫描所有LocalEventHandler和DistributedEventHandler分别注册到AbpLocalEventBusOptionsh和AbpDistributedEventBusOptions。
[DependsOn(
typeof(AbpEventBusAbstractionsModule),
typeof(AbpMultiTenancyModule),
typeof(AbpJsonModule),
typeof(AbpGuidsModule),
typeof(AbpBackgroundWorkersModule),
typeof(AbpDistributedLockingAbstractionsModule)
)]
public class AbpEventBusModule : AbpModule
{
public override void PreConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context)
{
AddEventHandlers(context.Services);
}
//...
private static void AddEventHandlers(IServiceCollection services)
{
var localHandlers = new List<Type>();
var distributedHandlers = new List<Type>();
// 扫描项目中的Handlers
services.OnRegistred(context =>
{
if (ReflectionHelper.IsAssignableToGenericType(context.ImplementationType, typeof(ILocalEventHandler<>)))
{
localHandlers.Add(context.ImplementationType);
}
else if (ReflectionHelper.IsAssignableToGenericType(context.ImplementationType, typeof(IDistributedEventHandler<>)))
{
distributedHandlers.Add(context.ImplementationType);
}
});
// 存储LocalHandlers和DistributedHandlers到各自Options中
services.Configure<AbpLocalEventBusOptions>(options =>
{
options.Handlers.AddIfNotContains(localHandlers);
});
services.Configure<AbpDistributedEventBusOptions>(options =>
{
options.Handlers.AddIfNotContains(distributedHandlers);
});
}
}
这两个Options将贯穿后续EventBus。
public class AbpLocalEventBusOptions
{
public ITypeList<IEventHandler> Handlers { get; }
}
public class AbpDistributedEventBusOptions
{
public ITypeList<IEventHandler> Handlers { get; }
public OutboxConfigDictionary Outboxes { get; }
public InboxConfigDictionary Inboxes { get; }
}
EventHandlerFactory
在上层使用中,对于Handler的实例化不是直接操作Handler,借助于EventHandlerFactory再封装一层。
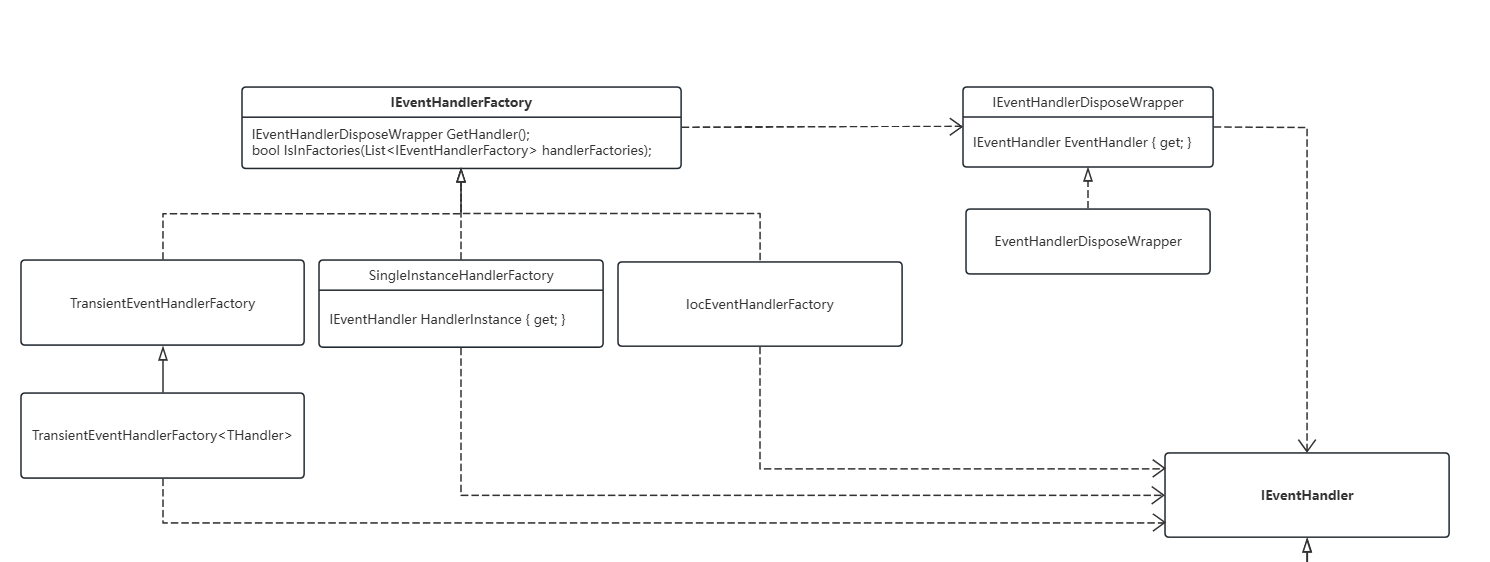 以IocEventHandlerFactory为例,在构造Factory时则存入EventHandlerType,当需要使用Handler时,则调用Factory.GetHandler来实例化一个Handler并将其包装到EventHandlerDisposeWrapper中。
以IocEventHandlerFactory为例,在构造Factory时则存入EventHandlerType,当需要使用Handler时,则调用Factory.GetHandler来实例化一个Handler并将其包装到EventHandlerDisposeWrapper中。
public class IocEventHandlerFactory : IEventHandlerFactory, IDisposable
{
public Type HandlerType { get; }
protected IServiceScopeFactory ScopeFactory { get; }
public IocEventHandlerFactory(IServiceScopeFactory scopeFactory, Type handlerType)
{
ScopeFactory = scopeFactory;
HandlerType = handlerType;
}
/// <summary>
/// Resolves handler object from Ioc container.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Resolved handler object</returns>
public IEventHandlerDisposeWrapper GetHandler()
{
var scope = ScopeFactory.CreateScope();
return new EventHandlerDisposeWrapper(
(IEventHandler)scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService(HandlerType),
() => scope.Dispose()
);
}
public bool IsInFactories(List<IEventHandlerFactory> handlerFactories)
{
return handlerFactories
.OfType<IocEventHandlerFactory>()
.Any(f => f.HandlerType == HandlerType);
}
public void Dispose()
{
}
}
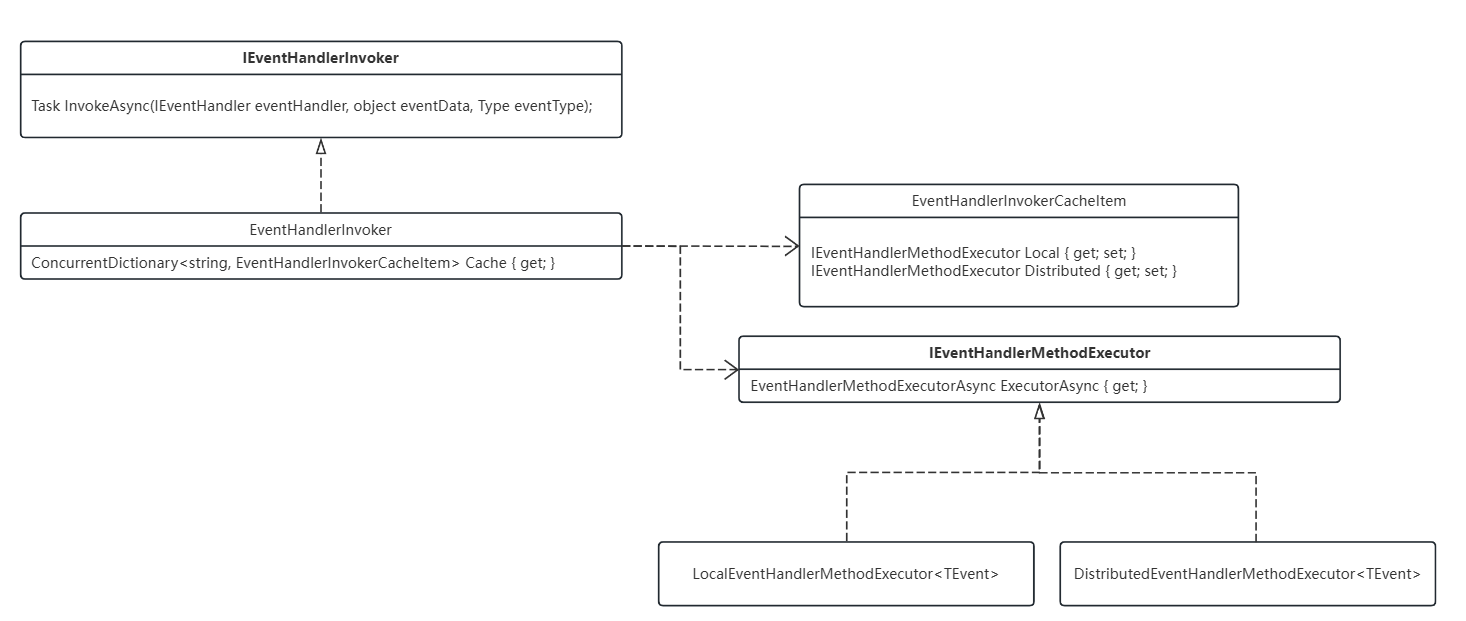
EventHandlerInvoker
和Factory的封装类似,对于Handler,不直接调用Handler的执行方法,而是再封装一层。ABP中封装了IEventHandler,内部实现缓存来管理Handler的执行。
public class EventHandlerInvoker : IEventHandlerInvoker, ISingletonDependency
{
private readonly ConcurrentDictionary<string, EventHandlerInvokerCacheItem> _cache;
public EventHandlerInvoker()
{
_cache = new ConcurrentDictionary<string, EventHandlerInvokerCacheItem>();
}
public async Task InvokeAsync(IEventHandler eventHandler, object eventData, Type eventType)
{
// 获得EventHandlerMethodExecutor实例并缓存
var cacheItem = _cache.GetOrAdd($"{eventHandler.GetType().FullName}-{eventType.FullName}", _ =>
{
var item = new EventHandlerInvokerCacheItem();
if (typeof(ILocalEventHandler<>).MakeGenericType(eventType).IsInstanceOfType(eventHandler))
{
item.Local = (IEventHandlerMethodExecutor)Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(LocalEventHandlerMethodExecutor<>).MakeGenericType(eventType));
}
if (typeof(IDistributedEventHandler<>).MakeGenericType(eventType).IsInstanceOfType(eventHandler))
{
item.Distributed = (IEventHandlerMethodExecutor)Activator.CreateInstance(typeof(DistributedEventHandlerMethodExecutor<>).MakeGenericType(eventType));
}
return item;
});
// 执行EventHandlerMethodExecutor的执行方法,进入到Handler中
if (cacheItem.Local != null)
{
// 执行EventHandlerMethodExecutor的执行方法
await cacheItem.Local.ExecutorAsync(eventHandler, eventData);
}
if (cacheItem.Distributed != null)
{
await cacheItem.Distributed.ExecutorAsync(eventHandler, eventData);
}
//...
}
}
具体的执行方法也进行了封装IEventHandlerMethodExecutor,该实现内部才是调用HandlerEventAsync方法所在。
public class LocalEventHandlerMethodExecutor<TEvent> : IEventHandlerMethodExecutor
where TEvent : class
{
public EventHandlerMethodExecutorAsync ExecutorAsync => (target, parameter) => target.As<ILocalEventHandler<TEvent>>().HandleEventAsync(parameter.As<TEvent>());
public Task ExecuteAsync(IEventHandler target, TEvent parameters)
{
return ExecutorAsync(target, parameters);
}
}
public class DistributedEventHandlerMethodExecutor<TEvent> : IEventHandlerMethodExecutor
where TEvent : class
{
public EventHandlerMethodExecutorAsync ExecutorAsync => (target, parameter) => target.As<IDistributedEventHandler<TEvent>>().HandleEventAsync(parameter.As<TEvent>());
public Task ExecuteAsync(IEventHandler target, TEvent parameters)
{
return ExecutorAsync(target, parameters);
}
}
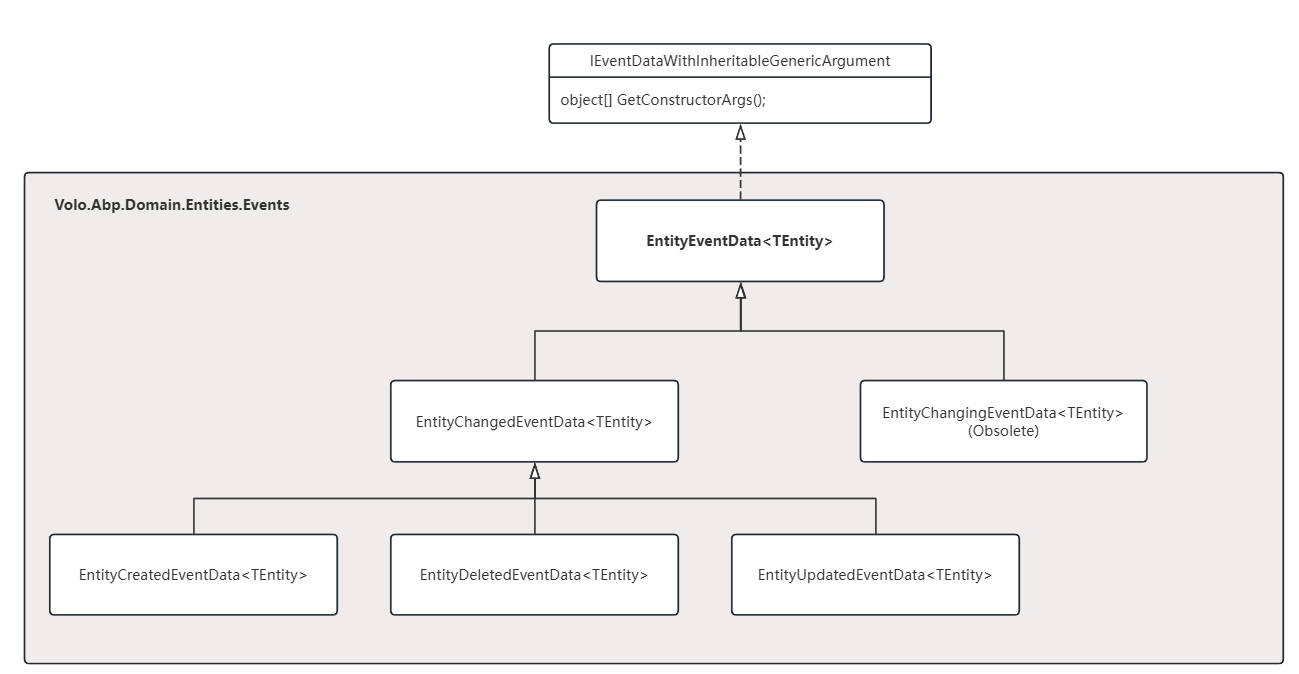
该部分类图简要如下
EventBus
LocalEventBus
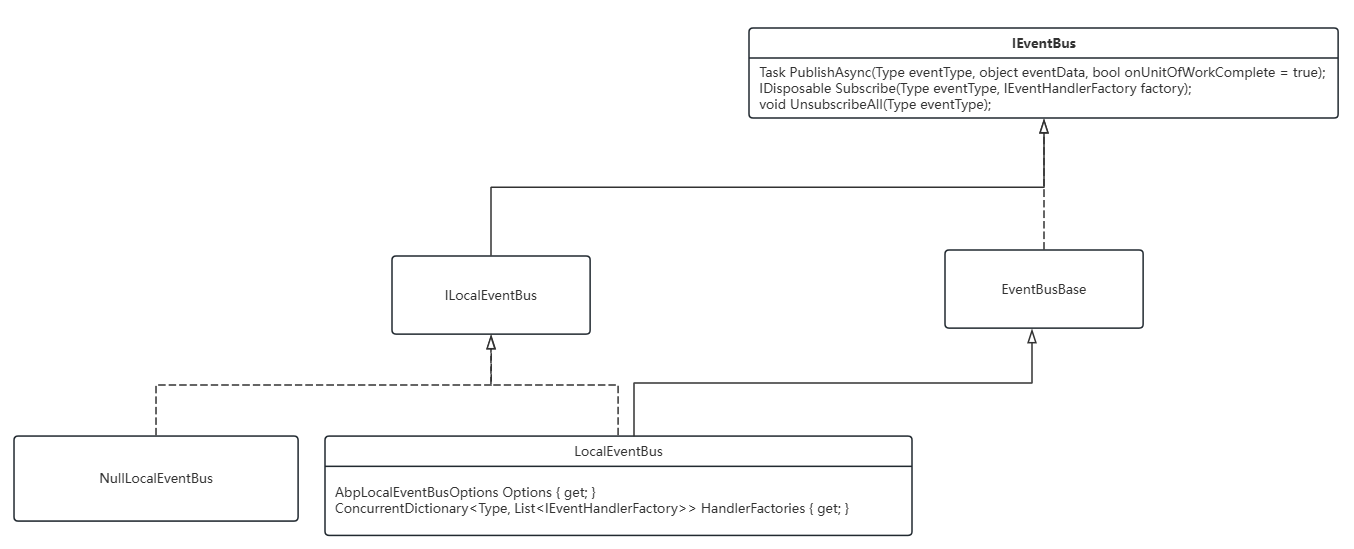
Subscribe
生命周期为单例,当初始化LocalEventBus时,会从上一节的AbpLocalEventBusOptions中获取所有Handlers,再按照Handlers所处理的类型分组整理成字典集合。
[ExposeServices(typeof(ILocalEventBus), typeof(LocalEventBus))]
public class LocalEventBus : EventBusBase, ILocalEventBus, ISingletonDependency
{
protected AbpLocalEventBusOptions Options { get; }
protected ConcurrentDictionary<Type, List<IEventHandlerFactory>> HandlerFactories { get; }
public LocalEventBus(
IOptions<AbpLocalEventBusOptions> options,
IServiceScopeFactory serviceScopeFactory,
ICurrentTenant currentTenant,
IUnitOfWorkManager unitOfWorkManager,
IEventHandlerInvoker eventHandlerInvoker)
: base(serviceScopeFactory, currentTenant, unitOfWorkManager, eventHandlerInvoker)
{
Options = options.Value;
Logger = NullLogger<LocalEventBus>.Instance;
HandlerFactories = new ConcurrentDictionary<Type, List<IEventHandlerFactory>>();
SubscribeHandlers(Options.Handlers);
}
protected virtual void SubscribeHandlers(ITypeList<IEventHandler> handlers)
{
foreach (var handler in handlers)
{
var interfaces = handler.GetInterfaces();
foreach (var @interface in interfaces)
{
if (!typeof(IEventHandler).GetTypeInfo().IsAssignableFrom(@interface))
{
continue;
}
// 获取事件类型
var genericArgs = @interface.GetGenericArguments();
if (genericArgs.Length == 1)
{
Subscribe(genericArgs[0], new IocEventHandlerFactory(ServiceScopeFactory, handler));
}
}
}
}
public override IDisposable Subscribe(Type eventType, IEventHandlerFactory factory)
{
// 按照类型,将包装了Handler的Factory加入到对应Factory集合中
GetOrCreateHandlerFactories(eventType)
.Locking(factories =>
{
if (!factory.IsInFactories(factories))
{
factories.Add(factory);
}
}
);
return new EventHandlerFactoryUnregistrar(this, eventType, factory);
}
private List<IEventHandlerFactory> GetOrCreateHandlerFactories(Type eventType)
{
return HandlerFactories.GetOrAdd(eventType, (type) => new List<IEventHandlerFactory>());
}
//...
}
简要过程如下
初始化后从AbpLocalEventBusOptions得到所有LocalHandlers
解析每一个Handler继承接口所声明的参数,例如,找到ILocalEventHandler的泛型类型StockCountChangedEvent。
public class MyHandler : ILocalEventHandler<StockCountChangedEvent>, ITransientDependency
{
public async Task HandleEventAsync(StockCountChangedEvent eventData)
{
//TODO: your code that does something on the event
}
}
- 将这个事件参数类型对应一个IEventHandlerFactory集合。所有事件参数类型和对应的Handlers都会保存在HandlerFactories中。
HandlerFactories.GetOrAdd(eventType, (type) => new List<IEventHandlerFactory>())
HandlerFactories在LocalEventBus中定义为并发字典类型。
protected ConcurrentDictionary<Type, List<IEventHandlerFactory>> HandlerFactories { get; }
例如,事件类型,StockCountChangedEvent,会存入到字典中,类型作为key, MyHandler作为Eve。
| Type | List |
|---|---|
| StockCountChangedEvent | new IocEventHandlerFactory(ServiceScopeFactory, MyHandler ) |
| … |
Unsubscribe
对应于Subscribe,还有一个Unsubscribe,来解除事件参数类型关联的EventHandlers
public class LocalEventBus : EventBusBase, ILocalEventBus, ISingletonDependency
{
protected ConcurrentDictionary<Type, List<IEventHandlerFactory>> HandlerFactories { get; }
//...
public override void Unsubscribe(Type eventType, IEventHandler handler)
{
GetOrCreateHandlerFactories(eventType)
.Locking(factories =>
{
factories.RemoveAll(
factory =>
factory is SingleInstanceHandlerFactory &&
(factory as SingleInstanceHandlerFactory).HandlerInstance == handler
);
});
}
//...
}
该方法使用场景较少,可能在特定需求下要删除某些Handler的处理,类似于实现动态订阅。
Publish
当在使用eventbus,发送事件时,常见用法是
await _localEventBus.PublishAsync(new StockCountChangedEvent
{
ProductId = productId,
NewCount = newCount
});
在其内部,会因onUnitOWorkComplete参数的差异采用不同的方式。
public class LocalEventBus : EventBusBase, ILocalEventBus, ISingletonDependency
{
//...
public Task PublishAsync<TEvent>(TEvent eventData, bool onUnitOfWorkComplete = true)
where TEvent : class
{
return PublishAsync(typeof(TEvent), eventData, onUnitOfWorkComplete);
}
public virtual async Task PublishAsync(
Type eventType,
object eventData,
bool onUnitOfWorkComplete = true)
{
if (onUnitOfWorkComplete && UnitOfWorkManager.Current != null)
{
AddToUnitOfWork(
UnitOfWorkManager.Current,
new UnitOfWorkEventRecord(eventType, eventData, EventOrderGenerator.GetNext())
);
return;
}
await PublishToEventBusAsync(eventType, eventData);
}
protected override void AddToUnitOfWork(IUnitOfWork unitOfWork, UnitOfWorkEventRecord eventRecord)
{
unitOfWork.AddOrReplaceLocalEvent(eventRecord);
}
protected override async Task PublishToEventBusAsync(Type eventType, object eventData)
{
await PublishAsync(new LocalEventMessage(Guid.NewGuid(), eventData, eventType));
}
//...
}
onUnitOfWorkComplete(true)
当参数为true,且当前存在工作单元下,会进入AddToUnitOfWork方法内,其内部则是调用UnitOfWork,将当前的LocalEvent先临时存储在LocalEvents集合中。
public class UnitOfWork : IUnitOfWork, ITransientDependency
{
protected List<UnitOfWorkEventRecord> LocalEvents { get; } = new List<UnitOfWorkEventRecord>();
//...
public virtual void AddOrReplaceLocalEvent(
UnitOfWorkEventRecord eventRecord,
Predicate<UnitOfWorkEventRecord> replacementSelector = null)
{
// 注意传入的LocalEvents集合
AddOrReplaceEvent(LocalEvents, eventRecord, replacementSelector);
}
public virtual void AddOrReplaceEvent(
List<UnitOfWorkEventRecord> eventRecords,
UnitOfWorkEventRecord eventRecord,
Predicate<UnitOfWorkEventRecord> replacementSelector = null)
{
if (replacementSelector == null)
{
eventRecords.Add(eventRecord);
}
else
{
var foundIndex = eventRecords.FindIndex(replacementSelector);
if (foundIndex < 0)
{
eventRecords.Add(eventRecord);
}
else
{
eventRecords[foundIndex] = eventRecord;
}
}
}
//...
}
这种方式下,会在工作单元即将完成时才会循环遍历各LocalEvent并发布出去触发其对应的EventHandler。该部分代码在UnitOfWork中完成。
public class UnitOfWork : IUnitOfWork, ITransientDependency
{
protected List<UnitOfWorkEventRecord> LocalEvents { get; } = new List<UnitOfWorkEventRecord>();
protected IUnitOfWorkEventPublisher UnitOfWorkEventPublisher { get; }
//...
public virtual async Task CompleteAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
if (_isRolledback)
{
return;
}
PreventMultipleComplete();
try
{
_isCompleting = true;
await SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
while (LocalEvents.Any() || DistributedEvents.Any())
{
if (LocalEvents.Any())
{
var localEventsToBePublished = LocalEvents.OrderBy(e => e.EventOrder).ToArray();
LocalEvents.Clear();
// UnitOfWorkEventPublisher内部则是依赖EventBus发布
await UnitOfWorkEventPublisher.PublishLocalEventsAsync(
localEventsToBePublished
);
}
if (DistributedEvents.Any())
{
var distributedEventsToBePublished = DistributedEvents.OrderBy(e => e.EventOrder).ToArray();
DistributedEvents.Clear();
await UnitOfWorkEventPublisher.PublishDistributedEventsAsync(
distributedEventsToBePublished
);
}
await SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
}
await CommitTransactionsAsync();
IsCompleted = true;
await OnCompletedAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_exception = ex;
throw;
}
}
//...
}
如上提及的UnitOfWorkEventPublisher,是在EventBus上封装一层。内部还是调用LocalEventBus,此时传递的参数onUnitOfWorkComplete为false。
public class UnitOfWorkEventPublisher : IUnitOfWorkEventPublisher, ITransientDependency
{
private readonly ILocalEventBus _localEventBus;
//...
public async Task PublishLocalEventsAsync(IEnumerable<UnitOfWorkEventRecord> localEvents)
{
foreach (var localEvent in localEvents)
{
await _localEventBus.PublishAsync(
localEvent.EventType,
localEvent.EventData,
onUnitOfWorkComplete: false
);
}
}
//...
}

onUnitOfWorkComplete(false)
当传参false时,则会按照发送事件类型找到在初始化阶段注册好的HandlerFactories中搜寻类型对应的Handler,再执行调用。
public class LocalEventBus : EventBusBase, ILocalEventBus, ISingletonDependency
{
//...
public virtual async Task PublishAsync(LocalEventMessage localEventMessage)
{
await TriggerHandlersAsync(localEventMessage.EventType, localEventMessage.EventData);
}
protected virtual async Task TriggerHandlersAsync(Type eventType, object eventData, List<Exception> exceptions, InboxConfig inboxConfig = null)
{
await new SynchronizationContextRemover();
// 按照事件类型得到关联的HandlerFactory
foreach (var handlerFactories in GetHandlerFactories(eventType))
{
foreach (var handlerFactory in handlerFactories.EventHandlerFactories)
{
// 得到HandlerFactory中的Handler,传参调用Handler的执行方法
await TriggerHandlerAsync(handlerFactory, handlerFactories.EventType, eventData, exceptions, inboxConfig);
}
}
// 泛型事件参数Handler下的事件处理
if (eventType.GetTypeInfo().IsGenericType &&
eventType.GetGenericArguments().Length == 1 &&
typeof(IEventDataWithInheritableGenericArgument).IsAssignableFrom(eventType))
{
var genericArg = eventType.GetGenericArguments()[0];
var baseArg = genericArg.GetTypeInfo().BaseType;
if (baseArg != null)
{
var baseEventType = eventType.GetGenericTypeDefinition().MakeGenericType(baseArg);
var constructorArgs = ((IEventDataWithInheritableGenericArgument)eventData).GetConstructorArgs();
var baseEventData = Activator.CreateInstance(baseEventType, constructorArgs);
// 该方法最终也还是进入到TriggerHandlerAsync
await PublishToEventBusAsync(baseEventType, baseEventData);
}
}
}
// 核心方法,执行Handler的处理逻辑
protected virtual async Task TriggerHandlerAsync(IEventHandlerFactory asyncHandlerFactory, Type eventType,
object eventData, List<Exception> exceptions, InboxConfig inboxConfig = null)
{
using (var eventHandlerWrapper = asyncHandlerFactory.GetHandler())
{
//...
// 通过EventHandler类型找到匹配的InboxConfig(该部分代码仅用于DistributedEventBus,此处可忽视该段代码)
var handlerType = eventHandlerWrapper.EventHandler.GetType();
if (inboxConfig?.HandlerSelector != null && !inboxConfig.HandlerSelector(handlerType))
{
return;
}
// 设置当前执行环境的租户
using (CurrentTenant.Change(GetEventDataTenantId(eventData)))
{
// 调用进入到Handler的方法中,在上一节中提及EventHandlerInvoker
await EventHandlerInvoker.InvokeAsync(eventHandlerWrapper.EventHandler, eventData, eventType);
}
//...
}
}
//...
}
如上对应于泛型事件参数的使用,对应于文档中提及的如下用法,主要是EntityChangedEventData这类泛型类。
public class MyHandler : ILocalEventHandler<EntityCreatedEventData<IdentityUser>>, ITransientDependency
{
/
}
 在Publish中,通过判别是否继承IEventDataWithInheritableGenericArgument以此来判断是否是泛型事件参数,从而再找到实际事件类型和对应的HandlerFactory再进行发送处理。
在Publish中,通过判别是否继承IEventDataWithInheritableGenericArgument以此来判断是否是泛型事件参数,从而再找到实际事件类型和对应的HandlerFactory再进行发送处理。
简要描述下整体思路:
项目启动阶段收集所有Handler注册到AbpLocalEventBusOptions中。
实例化LocalEventBus阶段,从Options中遍历事件类型及事件对应Handler组合到HandlerFactory,分类构建成HandlerFactories字典。
发送事件时,调用LocalEventBus.PublishAsync方法,根据参数onUnitOfWorkComplete决定是否立即发送(false)还是待工作单元即将完成时发送(true),如果是待工作单元即将完成,则等到工作单元执行完成方法时,其内部再次调用发送事件,此时onUnitOfWorkComplete传参为false进入4步骤;如果是立即发送,则直接进入4步骤。
实际的发送事件中,其内部根据发送的事件类型,从HandlerFactories中找到事件类型对应的HandlerFactory,再从Factory得到具体的Handler
借助EventHandlerInvoker来管理Handler的执行,EventHandlerInvoker内部使用EventHandlerMethodExecutor来实际调用Handler的HandleEventAsync方法。
进入到LocalEventHandler的HandleEventAsync方法内执行逻辑处理。
DistributedEventBus
分布式事件相对于本地事件,解耦的更彻底,通常借助于MQ来实现微服务间或者应用间的解耦。
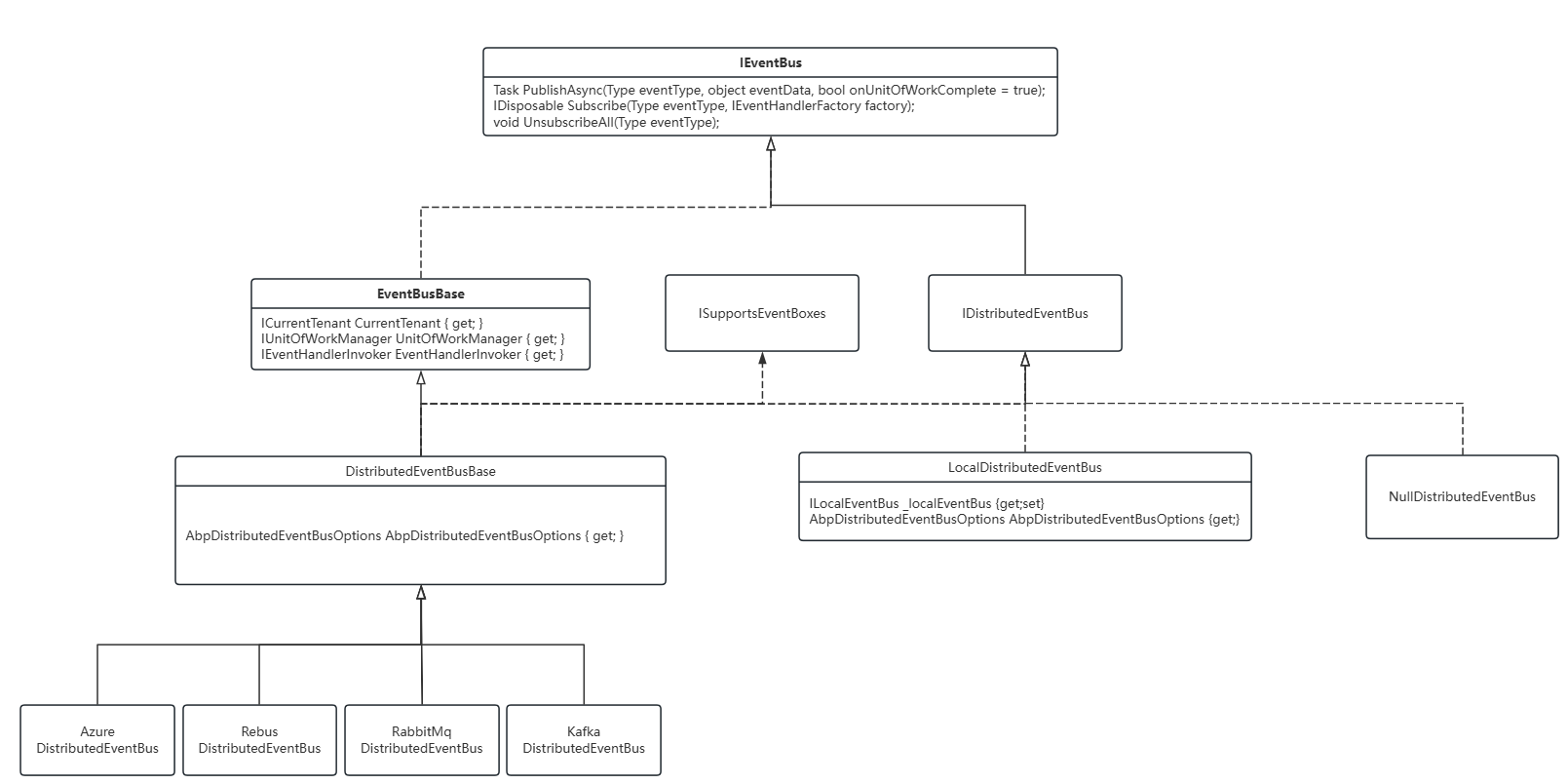 随着服务间使用的MQ不同,其实现也有相应的版本,默认ABP实现了如下几个版本
随着服务间使用的MQ不同,其实现也有相应的版本,默认ABP实现了如下几个版本
LocalDistributedEventBus,当没有选定MQ时,使用这个实现,其内部则使用上一节的LocalEventBus,作为本地事件来处理,场景更限制于单个服务上,事件无法应用到其他微服务/应用中。
RabbitMqDistributedEventBus,内部使用RabbitMq的包,将服务作为队列名注册到RabbitMq中,以及利用RabbitMq订阅消息,再转换到EventHandler处理。
KafkaDistributedEventBus,内部使用Kafka的包,过程和RabbitMq类似。
AzureDistributedEventBus,内部使用AzureServiceBus的包,过程和RabbitMq类似。
RebusDistributedEventBus,内部使用Rebus的包,过程和RabbitMq类似。
Subscribe
项目启动时会先调用各DistributedEventBus内初始化方法,执行和LocalEventBus相同的Subscribe方法,从AbpDistributedEventBusOptions中获取所有Handlers,再按照Handlers所处理的类型分组整理成字典集合。
例如RabbitMqDistrubutedEventBus,在应用启动时执行初始化
[DependsOn(
typeof(AbpEventBusModule),
typeof(AbpRabbitMqModule))]
public class AbpEventBusRabbitMqModule : AbpModule
{
public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context)
{
var configuration = context.Services.GetConfiguration();
Configure<AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions>(configuration.GetSection("RabbitMQ:EventBus"));
}
public override void OnApplicationInitialization(ApplicationInitializationContext context)
{
context
.ServiceProvider
.GetRequiredService<RabbitMqDistributedEventBus>()
.Initialize();
}
}
方法内部,则还是调用到SubscribeHandlers,所有事件类型及对应HandlerFactory保存在HanderFactories字典中。
public class RabbitMqDistributedEventBus : DistributedEventBusBase, ISingletonDependency
{
protected AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions { get; }
protected ConcurrentDictionary<Type, List<IEventHandlerFactory>> HandlerFactories { get; }
//...
public void Initialize()
{
// 注册消费者
Consumer = MessageConsumerFactory.Create(
new ExchangeDeclareConfiguration(
AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions.ExchangeName,
type: AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions.GetExchangeTypeOrDefault(),
durable: true
),
new QueueDeclareConfiguration(
AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions.ClientName,
durable: true,
exclusive: false,
autoDelete: false
),
AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions.ConnectionName
);
// 绑定收到MQ的消息后的后续处理
Consumer.OnMessageReceived(ProcessEventAsync);
SubscribeHandlers(AbpDistributedEventBusOptions.Handlers);
}
//...
}
对于AzureEventBus,KafkaEventBus和RebusEventBus都是如此,在应用启动时调用初始化方法。
Unsubscribe
和LocalEventBus中作用相同,解除事件参数类型关联的EventHandlers,使用场景较少,其作用在一些特定场景下解除绑定,比如只允许一次生效等场景。
public DistributedEventBus : DistributedEventBusBase, ISingletonDependency
{
protected ConcurrentDictionary<Type, List<IEventHandlerFactory>> HandlerFactories { get; }
//...
public override void Unsubscribe<TEvent>(Func<TEvent, Task> action)
{
Check.NotNull(action, nameof(action));
GetOrCreateHandlerFactories(typeof(TEvent))
.Locking(factories =>
{
factories.RemoveAll(
factory =>
{
var singleInstanceFactory = factory as SingleInstanceHandlerFactory;
if (singleInstanceFactory == null)
{
return false;
}
var actionHandler = singleInstanceFactory.HandlerInstance as ActionEventHandler<TEvent>;
if (actionHandler == null)
{
return false;
}
return actionHandler.Action == action;
});
});
}
//...
}
Publish
发布事件时,因需要考虑到分布式事务的处理,在发布参数上有些不同。主要考虑是否要在当前工作单元即将完成后发送事件,事件也往往定义成过去时,比如orderCreated, orderCompleted等完成时。
public abstract class DistributedEventBusBase : EventBusBase, IDistributedEventBus, ISupportsEventBoxes
{
//...
public async Task PublishAsync(
Type eventType,
object eventData,
bool onUnitOfWorkComplete = true,
bool useOutbox = true)
{
// 当前有工作单元下且设定在工作单元快完成时发送事件。
if (onUnitOfWorkComplete && UnitOfWorkManager.Current != null)
{
AddToUnitOfWork(
UnitOfWorkManager.Current,
new UnitOfWorkEventRecord(eventType, eventData, EventOrderGenerator.GetNext(), useOutbox)
);
return;
}
// 使用Outbox模式,将事件记录到本地消息表中
if (useOutbox)
{
if (await AddToOutboxAsync(eventType, eventData))
{
return;
}
}
// 直接发送事件到MQ或接收者(未配置MQ时使用LocalDistributedEventBus)
await PublishToEventBusAsync(eventType, eventData);
}
//...
}
如上有三种处理逻辑,每一个拎出来细化。
onUnitOfWorkComplete(true)
在参数onUnitOfWorkComplete为true且当前开启了工作单元下将分布式事件加入到当前工作单元内。
public abstract class DistributedEventBusBase : EventBusBase, IDistributedEventBus, ISupportsEventBoxes
{
protected override void AddToUnitOfWork(IUnitOfWork unitOfWork, UnitOfWorkEventRecord eventRecord)
{
unitOfWork.AddOrReplaceDistributedEvent(eventRecord);
}
}
在UnitOfWork内,则会将待发布的分布式事件保存在DistributedEvents集合中。
public class UnitOfWork : IUnitOfWork, ITransientDependency
{
//...
protected List<UnitOfWorkEventRecord> DistributedEvents { get; } = new List<UnitOfWorkEventRecord>();
//...
public virtual void AddOrReplaceDistributedEvent(
UnitOfWorkEventRecord eventRecord,
Predicate<UnitOfWorkEventRecord> replacementSelector = null)
{
AddOrReplaceEvent(DistributedEvents, eventRecord, replacementSelector);
}
public virtual void AddOrReplaceEvent(
List<UnitOfWorkEventRecord> eventRecords,
UnitOfWorkEventRecord eventRecord,
Predicate<UnitOfWorkEventRecord> replacementSelector = null)
{
if (replacementSelector == null)
{
eventRecords.Add(eventRecord);
}
else
{
var foundIndex = eventRecords.FindIndex(replacementSelector);
if (foundIndex < 0)
{
eventRecords.Add(eventRecord);
}
else
{
eventRecords[foundIndex] = eventRecord;
}
}
}
}
当整个工作单元即将完成,则再次调用DistributedEventBus,将保存好的分布式事件发送出去。此次发送则标记onUnitOfWorkComplete为false。
public class UnitOfWork : IUnitOfWork, ITransientDependency
{
//...
protected List<UnitOfWorkEventRecord> DistributedEvents { get; } = new List<UnitOfWorkEventRecord>();
protected IUnitOfWorkEventPublisher UnitOfWorkEventPublisher { get; }
//...
public virtual async Task CompleteAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
if (_isRolledback)
{
return;
}
PreventMultipleComplete();
try
{
_isCompleting = true;
await SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
while (LocalEvents.Any() || DistributedEvents.Any())
{
if (LocalEvents.Any())
{
var localEventsToBePublished = LocalEvents.OrderBy(e => e.EventOrder).ToArray();
LocalEvents.Clear();
await UnitOfWorkEventPublisher.PublishLocalEventsAsync(
localEventsToBePublished
);
}
if (DistributedEvents.Any())
{
var distributedEventsToBePublished = DistributedEvents.OrderBy(e => e.EventOrder).ToArray();
DistributedEvents.Clear();
await UnitOfWorkEventPublisher.PublishDistributedEventsAsync(
distributedEventsToBePublished
);
}
await SaveChangesAsync(cancellationToken);
}
await CommitTransactionsAsync();
IsCompleted = true;
await OnCompletedAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_exception = ex;
throw;
}
}
}
此处同样会借助UnitOfWorkEventPublisher,其内部封装了DistributedEventBus,此时的onUnitOfWorkComplete参数为false;
public class UnitOfWorkEventPublisher : IUnitOfWorkEventPublisher, ITransientDependency
{
//...
private readonly IDistributedEventBus _distributedEventBus;
//...
public async Task PublishDistributedEventsAsync(IEnumerable<UnitOfWorkEventRecord> distributedEvents)
{
foreach (var distributedEvent in distributedEvents)
{
await _distributedEventBus.PublishAsync(
distributedEvent.EventType,
distributedEvent.EventData,
onUnitOfWorkComplete: false,
useOutbox: distributedEvent.UseOutbox
);
}
}
}
 如上过程简要描述下,因存在一个循环,主要是参数差异(onUnitOfWorkComplete)。
如上过程简要描述下,因存在一个循环,主要是参数差异(onUnitOfWorkComplete)。
从DistributedEventBus.Publish(onUnitOfWorkComplete=true)调用到UnitOfWork.AddOrReplaceEvent,将待发布分布式事件存储到UnitOfWork.DistributedEvents中。
当前工作单元即将完成,从UnitOfWork.Complete又调用到DistributedEventBus.Publish(onUnitOfWorkComplete=false),将待发布的分布式事件发送,但不再回到第1步的处理过程,,而是取决于useOutbux,是存储到表待发还是直接发送。
onUnitOfWorkComplete(false)&useOutbox(true)
当useOutbox为true时,则保存事件到本地消息表中,保存时共享当前所在的工作单元,如果当前没有工作单元,则改为直接发送到MQ或LocalHandler。Inbox&Outbox模式见下节。
public abstract class DistributedEventBusBase : EventBusBase, IDistributedEventBus, ISupportsEventBoxes
{
//...
public async Task PublishAsync(
Type eventType,
object eventData,
bool onUnitOfWorkComplete = true,
bool useOutbox = true)
{
//...
// 使用Outbox模式,将事件记录到本地消息表中
if (useOutbox)
{
if (await AddToOutboxAsync(eventType, eventData))
{
return;
}
}
// 直接发送事件到MQ或接收者(未配置MQ时使用LocalDistributedEventBus)
await PublishToEventBusAsync(eventType, eventData);
}
private async Task<bool> AddToOutboxAsync(Type eventType, object eventData)
{
//共享当前工作单元
var unitOfWork = UnitOfWorkManager.Current;
if (unitOfWork == null)
{
return false;
}
foreach (var outboxConfig in AbpDistributedEventBusOptions.Outboxes.Values.OrderBy(x => x.Selector is null))
{
if (outboxConfig.Selector == null || outboxConfig.Selector(eventType))
{
var eventOutbox =
(IEventOutbox)unitOfWork.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService(outboxConfig.ImplementationType);
var eventName = EventNameAttribute.GetNameOrDefault(eventType);
await eventOutbox.EnqueueAsync(
new OutgoingEventInfo(
GuidGenerator.Create(),
eventName,
Serialize(eventData),
Clock.Now
)
);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
保存在消息表中后,ABP设计了单独的BackgroundWorker,定期扫描表将事件发送到MQ。
public class OutboxSenderManager : IBackgroundWorker
{
//...
public async Task StartAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
foreach (var outboxConfig in Options.Outboxes.Values)
{
if (outboxConfig.IsSendingEnabled)
{
var sender = ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IOutboxSender>();
await sender.StartAsync(outboxConfig, cancellationToken);
Senders.Add(sender);
}
}
}
/...
}
public class OutboxSender : IOutboxSender, ITransientDependency
{
//...
protected virtual async Task PublishOutgoingMessagesAsync(List<OutgoingEventInfo> waitingEvents)
{
foreach (var waitingEvent in waitingEvents)
{
// 发送分布式事件到MQ中
await DistributedEventBus
.AsSupportsEventBoxes()
.PublishFromOutboxAsync(
waitingEvent,
OutboxConfig
);
await Outbox.DeleteAsync(waitingEvent.Id);
}
}
//...
}
onUnitOfWorkComplete(false)&useOutbox(false)
最后一种模式下,即useOutbox为false时,直接发送到MQ或LocalHandler,以RabbitMq为例,最终使用RabbitMq包中channel发送消息到RabbitMq中。对应于Azure,kafka和Rebus都是使用各自的包发送到自家MQ中。
public class RabbitMqDistributedEventBus : DistributedEventBusBase, ISingletonDependency
{
//...
protected async override Task PublishToEventBusAsync(Type eventType, object eventData)
{
await PublishAsync(eventType, eventData, null);
}
public Task PublishAsync(
Type eventType,
object eventData,
IBasicProperties properties,
Dictionary<string, object> headersArguments = null)
{
var eventName = EventNameAttribute.GetNameOrDefault(eventType);
var body = Serializer.Serialize(eventData);
return PublishAsync(eventName, body, properties, headersArguments);
}
protected virtual Task PublishAsync(
string eventName,
byte[] body,
IBasicProperties properties,
Dictionary<string, object> headersArguments = null,
Guid? eventId = null)
{
using (var channel = ConnectionPool.Get(AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions.ConnectionName).CreateModel())
{
return PublishAsync(channel, eventName, body, properties, headersArguments, eventId);
}
}
protected virtual Task PublishAsync(
IModel channel,
string eventName,
byte[] body,
IBasicProperties properties,
Dictionary<string, object> headersArguments = null,
Guid? eventId = null)
{
EnsureExchangeExists(channel);
if (properties == null)
{
properties = channel.CreateBasicProperties();
properties.DeliveryMode = RabbitMqConsts.DeliveryModes.Persistent;
}
if (properties.MessageId.IsNullOrEmpty())
{
properties.MessageId = (eventId ?? GuidGenerator.Create()).ToString("N");
}
SetEventMessageHeaders(properties, headersArguments);
// 发送消息到RabbitMq
channel.BasicPublish(
exchange: AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions.ExchangeName,
routingKey: eventName,
mandatory: true,
basicProperties: properties,
body: body
);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
//...
}
如果使用的是LocalDistributedEventBus,则其内部使用LocalEventBus,走本地事件方式就回归到上一节LocalEventBus中代码了。
public class LocalDistributedEventBus : IDistributedEventBus, ISingletonDependency
{
private readonly ILocalEventBus _localEventBus;
//...
protected override async Task PublishToEventBusAsync(Type eventType, object eventData)
{
await PublishAsync(new LocalEventMessage(Guid.NewGuid(), eventData, eventType));
}
public Task PublishAsync<TEvent>(TEvent eventData, bool onUnitOfWorkComplete = true)
where TEvent : class
{
return _localEventBus.PublishAsync(eventData, onUnitOfWorkComplete);
}
public Task PublishAsync(Type eventType, object eventData, bool onUnitOfWorkComplete = true)
{
return _localEventBus.PublishAsync(eventType, eventData, onUnitOfWorkComplete);
}
public Task PublishAsync<TEvent>(TEvent eventData, bool onUnitOfWorkComplete = true, bool useOutbox = true) where TEvent : class
{
return _localEventBus.PublishAsync(eventData, onUnitOfWorkComplete);
}
public Task PublishAsync(Type eventType, object eventData, bool onUnitOfWorkComplete = true, bool useOutbox = true)
{
return _localEventBus.PublishAsync(eventType, eventData, onUnitOfWorkComplete);
}
}
Inbox&Outbox
本地消息表作为解决分布式最终一致性的利器,在ABP中也实现了,尽管功能有限,不像DotNet Cap般强大,但总归还是能够处理一些分布式事务场景需求。如果想要在服务中使用上Inbox&Oubbox,则需要创建其对应表,ABP已经提前设计好了该部分实体及表。只需在DbContext中加入属性及模型配置即可。
public class AppDbContext : AbpDbContext<AppDbContext >
{
//...
public DbSet<OutgoingEventRecord> OutgoingEvents { get; set; }
public DbSet<IncomingEventRecord> IncomingEvents { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder builder)
{
//...
builder.ConfigureEventOutbox();
builder.ConfigureEventInbox();
}
}
Outbox
EventStorage
在DistributedEventBus一节中提及到了分布式事件会存到表中,即Outbox对应表。
public abstract class DistributedEventBusBase : EventBusBase, IDistributedEventBus, ISupportsEventBoxes
{
//...
private async Task<bool> AddToOutboxAsync(Type eventType, object eventData)
{
var unitOfWork = UnitOfWorkManager.Current;
if (unitOfWork == null)
{
return false;
}
foreach (var outboxConfig in AbpDistributedEventBusOptions.Outboxes.Values.OrderBy(x => x.Selector is null))
{
// 事件类型匹配是否该outboxConfig符合条件
if (outboxConfig.Selector == null || outboxConfig.Selector(eventType))
{
// 实例化具体类型的EventOutbox
var eventOutbox = (IEventOutbox)unitOfWork.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService(outboxConfig.ImplementationType);
var eventName = EventNameAttribute.GetNameOrDefault(eventType);
// 分布式事件入表
await eventOutbox.EnqueueAsync(
new OutgoingEventInfo(
GuidGenerator.Create(),
eventName,
Serialize(eventData),
Clock.Now
)
);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//...
}
OutboxConfig
在保存时,会先根据事件类型选择Outbox的配置,对应关系的存储在AbpDistributedEventBusOptions中。
public class AbpDistributedEventBusOptions
{
//...
public OutboxConfigDictionary Outboxes { get; }
//...
}
public class OutboxConfigDictionary : Dictionary<string, OutboxConfig>
{
public void Configure(Action<OutboxConfig> configAction)
{
Configure("Default", configAction);
}
public void Configure(string outboxName, Action<OutboxConfig> configAction)
{
var outboxConfig = this.GetOrAdd(outboxName, () => new OutboxConfig(outboxName));
configAction(outboxConfig);
}
}
public class OutboxConfig
{
public string Name { get; }
public Type ImplementationType { get; set; }
public Func<Type, bool> Selector { get; set; }
public bool IsSendingEnabled { get; set; } = true;
}
默认情况下,如果当前服务只有一个Database,在OutboxConfigDictionary中则是使用Default,服务注册时,如下配置即可。
Configure<AbpDistributedEventBusOptions>(options =>
{
options.Outboxes.Configure(config =>
{
config.MySQL<MyDbContext>();
});
});
当有多个Database时,则可以配置多个Outbox并且设置存储源,还能够过滤事件类型是否在这个Outbox上应用,从而实现对于事件类型能够分开处理。
Configure<AbpDistributedEventBusOptions>(options =>
{
options.Outboxes.Configure(config =>
{
config.MySQL<MyDbContext>();
});
options.Outboxes.Configure("second", config =>
{
config.UseMySQL<MySecondDbContext>();
});
options.Outboxes.Configure("third", config =>
{
config.UseMongoDbContext<MyMongoDbContext>();
config.Selector = eventType =>
{
return eventType == typeof(ProductCreatedEto);
};
});
});
在如上UseMySQL,UseMongbDbContex扩展方法中,实际上是对ImplementationType赋值。
public static void UseMySQL<TDbContext>(this OutboxConfig outboxConfig)
where TDbContext : IHasEventOutbox
{
outboxConfig.ImplementationType = typeof(ISqlRawDbContextEventOutbox<TDbContext>);
}
EventOutbox
当有了符合事件类型的OutboxConfig后,则是按照ImplementationType实例化相应的EventOutbox。
var eventOutbox = (IEventOutbox)unitOfWork.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService(outboxConfig.ImplementationType);
var eventName = EventNameAttribute.GetNameOrDefault(eventType);
对于EventOutbox因为存储源的的不同,分别做了实现。
 例如,当使用EfCore的DbContext时,存储分布式事件时,使用DbContext.Entity直接保存到表中。
例如,当使用EfCore的DbContext时,存储分布式事件时,使用DbContext.Entity直接保存到表中。
public class DbContextEventOutbox<TDbContext> : IDbContextEventOutbox<TDbContext>
where TDbContext : IHasEventOutbox
{
//...
[UnitOfWork]
public virtual async Task EnqueueAsync(OutgoingEventInfo outgoingEvent)
{
var dbContext = (IHasEventOutbox)await DbContextProvider.GetDbContextAsync();
dbContext.OutgoingEvents.Add(
new OutgoingEventRecord(outgoingEvent)
);
}
//...
}
最终,分布式事件存入到存储源中。
EventPublish
在之前提到了有个单独的线程将分布式事件发送到MQ中,此处细说,在AbpEventBusModule中,应用启动时会启动两个BackgroudWorker。
public class AbpEventBusModule : AbpModule
{
//...
public async override Task OnApplicationInitializationAsync(ApplicationInitializationContext context)
{
await context.AddBackgroundWorkerAsync<OutboxSenderManager>();
await context.AddBackgroundWorkerAsync<InboxProcessManager>();
}
//...
}
OutboxSenderManager会定期启动,扫描服务注册时配置好的多个OutboxConfig并交付给OutboxSender来执行读取存储的分布式事件及发送到MQ。
public class OutboxSenderManager : IBackgroundWorker
{
protected AbpDistributedEventBusOptions Options { get; }
protected IServiceProvider ServiceProvider { get; }
protected List<IOutboxSender> Senders { get; }
//...
public async Task StartAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
foreach (var outboxConfig in Options.Outboxes.Values)
{
if (outboxConfig.IsSendingEnabled)
{
var sender = ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IOutboxSender>();
await sender.StartAsync(outboxConfig, cancellationToken);
Senders.Add(sender);
}
}
}
//...
}
在OutboxSender内部,则是先进行读取
public class OutboxSender : IOutboxSender, ITransientDependency
{
protected IDistributedEventBus DistributedEventBus { get; }
protected IEventOutbox Outbox { get; private set; }
protected OutboxConfig OutboxConfig { get; private set; }
protected AbpEventBusBoxesOptions EventBusBoxesOptions { get; }
//...
protected virtual async Task RunAsync()
{
//...
while (true)
{
// 读取待发送的分布式事件
var waitingEvents = await Outbox.GetWaitingEventsAsync(EventBusBoxesOptions.OutboxWaitingEventMaxCount, StoppingToken);
if (waitingEvents.Count <= 0)
{
// 发送完毕则推出
break;
}
if (EventBusBoxesOptions.BatchPublishOutboxEvents)
{
// 批量发送
await PublishOutgoingMessagesInBatchAsync(waitingEvents);
}
else
{
// 单条发送
await PublishOutgoingMessagesAsync(waitingEvents);
}
}
//...
}
protected virtual async Task PublishOutgoingMessagesAsync(List<OutgoingEventInfo> waitingEvents)
{
foreach (var waitingEvent in waitingEvents)
{
// 通过EventBus发送
await DistributedEventBus
.AsSupportsEventBoxes()
.PublishFromOutboxAsync(
waitingEvent,
OutboxConfig
);
// 发送完毕删除存储的分布式事件记录
await Outbox.DeleteAsync(waitingEvent.Id);
//...
}
}
protected virtual async Task PublishOutgoingMessagesInBatchAsync(List<OutgoingEventInfo> waitingEvents)
{
// 通过EventBus发送
await DistributedEventBus
.AsSupportsEventBoxes()
.PublishManyFromOutboxAsync(waitingEvents, OutboxConfig);
// 发送完毕删除存储的分布式事件记录
await Outbox.DeleteManyAsync(waitingEvents.Select(x => x.Id).ToArray());
//...
}
}
最终还是回到了EventBus中发送事件,但EventBus有要求,必须要继承了ISupportsEventBoxes,其调用的方法来源于该接口中。
public interface ISupportsEventBoxes
{
Task PublishFromOutboxAsync(OutgoingEventInfo outgoingEvent, OutboxConfig outboxConfig);
Task PublishManyFromOutboxAsync(IEnumerable<OutgoingEventInfo> outgoingEvents, OutboxConfig outboxConfig);
Task ProcessFromInboxAsync(IncomingEventInfo incomingEvent, InboxConfig inboxConfig);
}
其实现为各Mq的EventBus,以RabbitMqDistributedEventBus为例,其内部直接使用channel发送事件到Mq,Azure,Kafka和Rebus均类似。
public class RabbitMqDistributedEventBus : DistributedEventBusBase, ISingletonDependency
{
//...
public async override Task PublishManyFromOutboxAsync(
IEnumerable<OutgoingEventInfo> outgoingEvents,
OutboxConfig outboxConfig)
{
using (var channel = ConnectionPool.Get(AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions.ConnectionName).CreateModel())
{
var outgoingEventArray = outgoingEvents.ToArray();
channel.ConfirmSelect();
foreach (var outgoingEvent in outgoingEventArray)
{
await PublishAsync(
channel,
outgoingEvent.EventName,
outgoingEvent.EventData,
properties: null,
eventId: outgoingEvent.Id);
}
channel.WaitForConfirmsOrDie();
}
}
//...
}
该部分类图简要如下
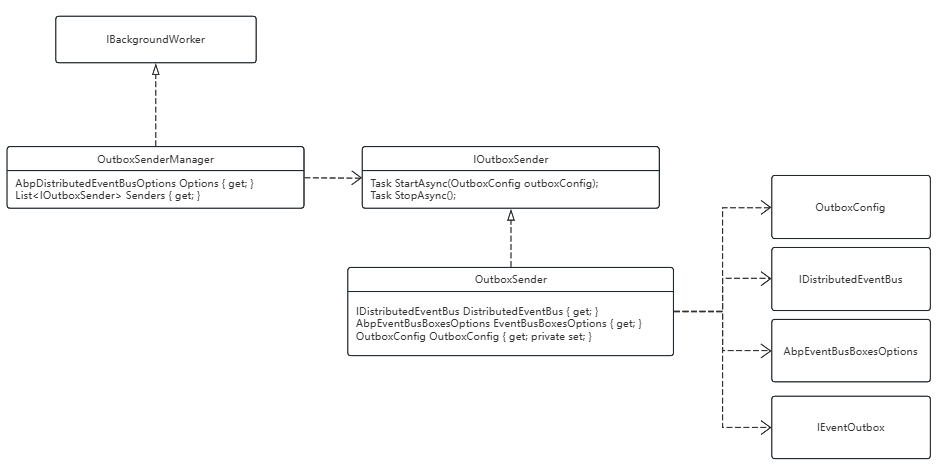 此处有一个控制参数,控制读取数量,发送失败间隔时间等,可在服务注册时对其配置,也可直接使用默认值。
此处有一个控制参数,控制读取数量,发送失败间隔时间等,可在服务注册时对其配置,也可直接使用默认值。
public class AbpEventBusBoxesOptions
{
public TimeSpan CleanOldEventTimeIntervalSpan { get; set; }
public int InboxWaitingEventMaxCount { get; set; }
public int OutboxWaitingEventMaxCount { get; set; }
public TimeSpan PeriodTimeSpan { get; set; }
public TimeSpan DistributedLockWaitDuration { get; set; }
public TimeSpan WaitTimeToDeleteProcessedInboxEvents { get; set; }
public bool BatchPublishOutboxEvents { get; set; }
}
Inbox
EventStorage
当处于MQ的另一端从Mq拉取到消息或MQ主动推送消息后,按照本地消息表的工作原理,需要先保存到表中。在各MQ的DistributedEventBus服务初始化时,提及到Handler的订阅过程,同时还有一个回调注册。例如在RabbitMqDistributedEventBus中,先注册消费者,同时设置了一个回调,用来接收MQ推送的消息触发回调ProcessEventAsync。
public class RabbitMqDistributedEventBus : DistributedEventBusBase, ISingletonDependency
{
protected AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions { get; }
protected ConcurrentDictionary<Type, List<IEventHandlerFactory>> HandlerFactories { get; }
//...
public void Initialize()
{
// 注册消费者
Consumer = MessageConsumerFactory.Create(
new ExchangeDeclareConfiguration(
AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions.ExchangeName,
type: AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions.GetExchangeTypeOrDefault(),
durable: true
),
new QueueDeclareConfiguration(
AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions.ClientName,
durable: true,
exclusive: false,
autoDelete: false
),
AbpRabbitMqEventBusOptions.ConnectionName
);
// 绑定收到MQ的消息后的后续处理
Consumer.OnMessageReceived(ProcessEventAsync);
SubscribeHandlers(AbpDistributedEventBusOptions.Handlers);
}
//...
}
该方法中,实现了收到MQ的消息后转换存储到本地表中。
public class RabbitMqDistributedEventBus : DistributedEventBusBase, ISingletonDependency
{
//...
private async Task ProcessEventAsync(IModel channel, BasicDeliverEventArgs ea)
{
var eventName = ea.RoutingKey;
var eventType = EventTypes.GetOrDefault(eventName);
if (eventType == null)
{
return;
}
var eventBytes = ea.Body.ToArray();
if (await AddToInboxAsync(ea.BasicProperties.MessageId, eventName, eventType, eventBytes))
{
return;
}
var eventData = Serializer.Deserialize(eventBytes, eventType);
await TriggerHandlersAsync(eventType, eventData);
}
//...
}
其中会分为两种场景处理:
如果没有使用上Inbox,事件则直接被触发,该触发逻辑与下一小节中的TriggerHandlersAsync为同一个方法,此处先不提及。
如果使用了Inbox,则会将事件存储到表中,再由下一小节的InboxProcessManager来推动事件触发。
public abstract class DistributedEventBusBase : EventBusBase, IDistributedEventBus, ISupportsEventBoxes
{
//...
protected async Task<bool> AddToInboxAsync(
string messageId,
string eventName,
Type eventType,
byte[] eventBytes)
{
if (AbpDistributedEventBusOptions.Inboxes.Count <= 0)
{
return false;
}
using (var scope = ServiceScopeFactory.CreateScope())
{
foreach (var inboxConfig in AbpDistributedEventBusOptions.Inboxes.Values.OrderBy(x => x.EventSelector is null))
{
// 事件类型匹配是否该inboxConfig符合条件
if (inboxConfig.EventSelector == null || inboxConfig.EventSelector(eventType))
{
// 实例化具体类型的EventInbox
var eventInbox = (IEventInbox)scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService(inboxConfig.ImplementationType);
if (!messageId.IsNullOrEmpty())
{
// 消息幂等校验,重复消息则去除
if (await eventInbox.ExistsByMessageIdAsync(messageId))
{
continue;
}
}
// 保存到存储源中
await eventInbox.EnqueueAsync(new IncomingEventInfo(
GuidGenerator.Create(),
messageId,
eventName,
eventBytes,
Clock.Now
)
);
}
}
}
return true;
}
//...
}
InboxConfig
在保存事件到表前,会先根据事件类型选择一个InboxConfig,类似于OutboxConfig,配置了一些存储源,过滤特定事件类型等。对应关系的存储在AbpDistributedEventBusOptions中。
public class AbpDistributedEventBusOptions
{
//...
public InboxConfigDictionary Inboxes { get; }
//...
}
public class InboxConfigDictionary : Dictionary<string, InboxConfig>
{
public void Configure(Action<InboxConfig> configAction)
{
Configure("Default", configAction);
}
public void Configure(string outboxName, Action<InboxConfig> configAction)
{
var outboxConfig = this.GetOrAdd(outboxName, () => new InboxConfig(outboxName));
configAction(outboxConfig);
}
}
public class InboxConfig
{
public string Name { get; }
public Type ImplementationType { get; set; }
public Func<Type, bool> EventSelector { get; set; }
public Func<Type, bool> HandlerSelector { get; set; }
public bool IsProcessingEnabled { get; set; } = true;
}
在服务注册时,可以进行配置。默认情况下,如果当前服务只有一个Database,在InboxConfigDictionary中则是使用Default,服务注册时,如下配置即可。
Configure<AbpDistributedEventBusOptions>(options =>
{
options.Inboxes.Configure(config =>
{
config.UseMySQL();
});
});
当有多个Database时,则可以配置多个Inbox并且设置存储源,还能够过滤事件类型是否在这个Inbox上应用,从而实现对于事件类型能够分开处理。
Configure<AbpDistributedEventBusOptions>(options =>
{
options.Inboxes.Configure(config =>
{
config.MySQL<MyDbContext>();
});
options.Inboxes.Configure("second", config =>
{
config.UseMySQL<MySecondDbContext>();
});
options.Inboxes.Configure("third", config =>
{
config.UseMongoDbContext<MyMongoDbContext>();
config.EventSelector = eventType =>
{
return eventType == typeof(ProductCreatedEto);
};
config.HandlerSelector = handlerType =>
{
return handlerType == typeof(ProductCreatedHandler);
};
});
});
在如上UseMySQL,UseMongbDbContex扩展方法中,实际上是对ImplementationType赋值。
public static void UseMySQL<TDbContext>(this InboxConfig inboxConfig)
where TDbContext : IHasEventInbox
{
inboxConfig.ImplementationType = typeof(ISqlRawDbContextEventOutbox<TDbContext>);
}
EventInBox
当有了符合事件类型的InConfig后,则是按照ImplementationType实例化相应的EventOutbox。
var eventInbox = (IEventInbox)scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService(inboxConfig.ImplementationType);
对于EventInbox因为存储源的的不同,分别做了实现。
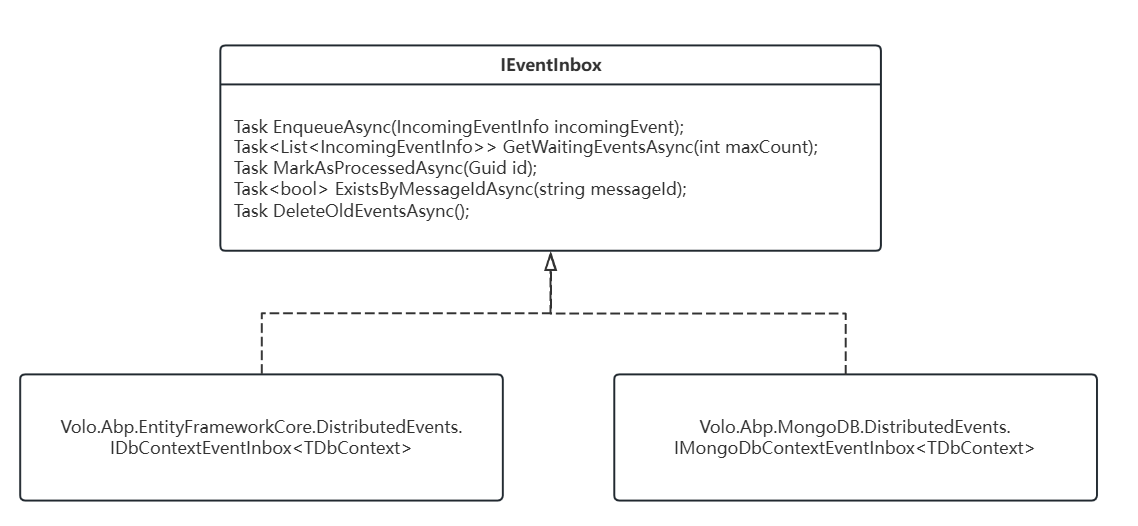 例如,当使用EfCore的DbContext时,存储分布式事件时,使用DbContext.Entity直接保存到表中。
例如,当使用EfCore的DbContext时,存储分布式事件时,使用DbContext.Entity直接保存到表中。
public class DbContextEventInbox<TDbContext> : IDbContextEventInbox<TDbContext>
where TDbContext : IHasEventInbox
{
//...
[UnitOfWork]
public virtual async Task EnqueueAsync(IncomingEventInfo incomingEvent)
{
var dbContext = await DbContextProvider.GetDbContextAsync();
dbContext.IncomingEvents.Add(
new IncomingEventRecord(incomingEvent)
);
}
//...
}
最终,分布式事件存入到存储源中。
EventTrigger
消息已经到表中,还需要实现匹配相应的Handler从而完成消费端对关注事件的处理逻辑。在AbpEventBusModule中,应用启动时除了OutboxSenderManager还有一个InboxProcessManager,来管理将收到的消息触发其对应的EventHandler。
public class AbpEventBusModule : AbpModule
{
//...
public async override Task OnApplicationInitializationAsync(ApplicationInitializationContext context)
{
await context.AddBackgroundWorkerAsync<OutboxSenderManager>();
await context.AddBackgroundWorkerAsync<InboxProcessManager>();
}
//...
}
这也是一个BackgroundWorker,循环所有的存储源,拿到InboxConfig移交给InboxProcessor来具体执行。
public class InboxProcessManager : IBackgroundWorker
{
protected AbpDistributedEventBusOptions Options { get; }
protected IServiceProvider ServiceProvider { get; }
protected List<IInboxProcessor> Processors { get; }
///...
public async Task StartAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
foreach (var inboxConfig in Options.Inboxes.Values)
{
if (inboxConfig.IsProcessingEnabled)
{
var processor = ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IInboxProcessor>();
await processor.StartAsync(inboxConfig, cancellationToken);
Processors.Add(processor);
}
}
}
public async Task StopAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken = default)
{
foreach (var processor in Processors)
{
await processor.StopAsync(cancellationToken);
}
}
}
public class InboxProcessor : IInboxProcessor, ITransientDependency
{
//...
protected IDistributedEventBus DistributedEventBus { get; }
protected InboxConfig InboxConfig { get; private set; }
protected AbpEventBusBoxesOptions EventBusBoxesOptions { get; }
//...
protected virtual async Task RunAsync()
{
// 删除过期的事件
await DeleteOldEventsAsync();
//...
while (true)
{
// 循环读取待处理状态的事件,直到全部读取完成
var waitingEvents = await Inbox.GetWaitingEventsAsync(EventBusBoxesOptions.InboxWaitingEventMaxCount, StoppingToken);
if (waitingEvents.Count <= 0)
{
break;
}
//...
foreach (var waitingEvent in waitingEvents)
{
using (var uow = UnitOfWorkManager.Begin(isTransactional: true, requiresNew: true))
{
// 通过事件类型从HanderFactories中找到符合条件的HandlerFactory再实现调用各Handler的方法
await DistributedEventBus
.AsSupportsEventBoxes()
.ProcessFromInboxAsync(waitingEvent, InboxConfig);
// 事件触发完成则标记完成状态
await Inbox.MarkAsProcessedAsync(waitingEvent.Id);
await uow.CompleteAsync();
}
//...
}
}
//...
}
}
如上使用的DistributedEventBus仍然需要是支持ISupportsEventBoxes接口的。以RabbitMqDistributedEventBus为例,
public class RabbitMqDistributedEventBus : DistributedEventBusBase, ISingletonDependency
{
//...
public async override Task ProcessFromInboxAsync(IncomingEventInfo incomingEvent, InboxConfig inboxConfig)
{
var eventType = EventTypes.GetOrDefault(incomingEvent.EventName);
if (eventType == null)
{
return;
}
var eventData = Serializer.Deserialize(incomingEvent.EventData, eventType);
var exceptions = new List<Exception>();
// 执行EventType找Handler完成触发逻辑
await TriggerHandlersAsync(eventType, eventData, exceptions, inboxConfig);
if (exceptions.Any())
{
ThrowOriginalExceptions(eventType, exceptions);
}
}
protected virtual async Task TriggerHandlersAsync(Type eventType, object eventData, List<Exception> exceptions, InboxConfig inboxConfig = null)
{
await new SynchronizationContextRemover();
// 按照事件类型得到关联的HandlerFactory
foreach (var handlerFactories in GetHandlerFactories(eventType))
{
// 得到HandlerFactory中的Handler,传参调用Handler的执行方法
foreach (var handlerFactory in handlerFactories.EventHandlerFactories)
{
await TriggerHandlerAsync(handlerFactory, handlerFactories.EventType, eventData, exceptions, inboxConfig);
}
}
// 泛型事件参数Handler下的事件处理(该部分仅用于LocalEvent,此处可忽略)
if (eventType.GetTypeInfo().IsGenericType &&
eventType.GetGenericArguments().Length == 1 &&
typeof(IEventDataWithInheritableGenericArgument).IsAssignableFrom(eventType))
{
//...
}
}
// 核心方法,执行Handler的处理逻辑
protected virtual async Task TriggerHandlerAsync(IEventHandlerFactory asyncHandlerFactory, Type eventType,
object eventData, List<Exception> exceptions, InboxConfig inboxConfig = null)
{
using (var eventHandlerWrapper = asyncHandlerFactory.GetHandler())
{
//...
// 通过EventHandler类型找到匹配的InboxConfig,再次匹配下Handler是否符合预先配置好的条件
var handlerType = eventHandlerWrapper.EventHandler.GetType();
if (inboxConfig?.HandlerSelector != null &&
!inboxConfig.HandlerSelector(handlerType))
{
return;
}
// 设置当前执行环境的租户
using (CurrentTenant.Change(GetEventDataTenantId(eventData)))
{
// 调用进入到Handler的方法中,在上一节中提及EventHandlerInvoker
await EventHandlerInvoker.InvokeAsync(eventHandlerWrapper.EventHandler, eventData, eventType);
}
}
}
//...
}
最终进入到EventHandlerInvoker中,则是进入到了EventHandler提及的小节。 该部分类图简要如下
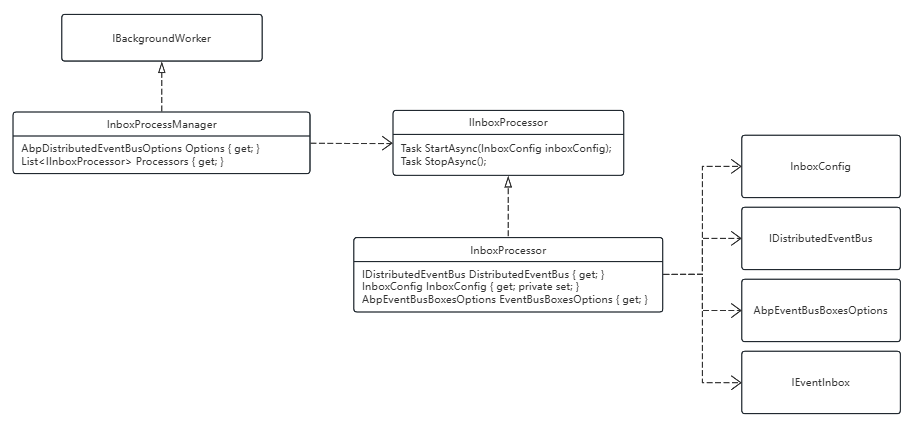
扩展
可扩展点非常之多,此处只简单提及几个。
实现自定义的DistributedEventBus,如实现基于Redis的,基于System.Net.Channels的,可参照RabbitMqDistributedEventBus少量修改。
扩展IEventHandlerInvoker,实现自定义的EventHandlerInvoker,在Handler执行前后增加一些功能。
重写EventBusBase中的TriggerHandlersAsync逻辑,在原有基础上再扩展功能。
2024-12-26,望技术有成后能回来看见自己的脚步。